
Topic 6
One of the most important uses of image interpretation in remote sensing is the production of Land Use and Land Cover maps.
Land Use: refers to the purpose the land serves, for example, recreation, wildlife habitat, or agriculture, urban development, and mostly areas impacted by human activity. Knowledge of land use helps us to develop strategies to balance conservation, conflicting uses, and developmental pressures. Some of the issues which are of concern include the removal or disturbance of productive land, urban encroachment, and depletion of forests.
Land Cover: refers to the surface cover whether vegetation, water, bare soil, urban development or other. Identifying, delineating and mapping land cover is important for global monitoring studies, resource management, and planning activities.
LU/LC Example 1: Portion of a CIR Airphoto, Hiawatha National Forest, Michigan

LU/LC Example 2: Portion of a B&W Airphoto, Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan

Land Use / Land Cover Classification Systems
For practical reasons, land use and land cover classification was combined into a single hierarchial system by the USGS and referred to as the USGS Land Use Land Cover Classification System.
USGS LU/LC Classification: The classification systems consists of four Levels.
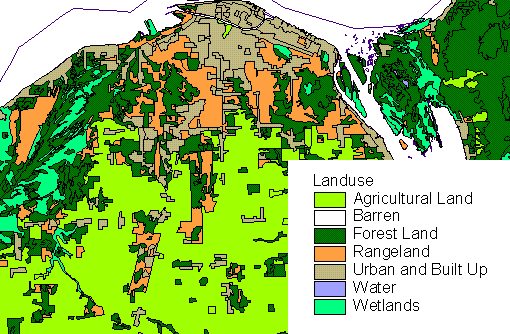
USGS Level I is the most general and allows for land classification at a small scale (>1:250,000) and is used for satellite imagery (Landsat).
| Level I Categories | |
| 1 | Urban or Built-up Land |
| 2 | Agricultural Land |
| 3 | Rangeland |
| 4 | Forest Land |
| 5 | Water |
| 6 | Wetland |
| 7 | Barren Land |
| 8 | Tundra |
| 9 | Perennial Ice or Snow |
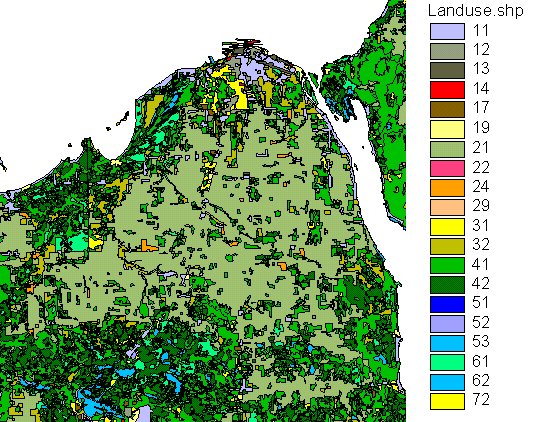
USGS Level II is a subdivision of Level I categories into related classes. This level of generalization is useful for airphotos at scales of about 1:80,000.
Level II Categories: (from
Michigan Land/Use Cover Classification System)
I URBAN & BUILT UP
11 Residential
12 Commercial, Services, & Institutional
13 Industrial
14 Transportation, Communication & Utilities
[15] Map Industrial Parks under appropriate category in
Commercial
Services & Institutional (12)
or Industrial (13)
16 Mixed
17 Extractive
19 Open & Other
2 AGRICULTURAL LAND
21 Cropland, Rotation & Permanent Pasture
22 Orchards, Bush-Fruits, Vineyards & Ornamental
Horticulture Areas
23 Confined Feeding Operations
[28] Inactive Land (These plant communities will be mapped under
herbaceous, rangelands (31).
29 Other Agricultural Land
3 RANGELAND
31 Herbaceous Rangeland
32 Shrub Rangeland
4 FOREST LAND
41 Broadleaved Forest (generally deciduous)
42 Coniferous Forest
43 Mixed Conifer-Broadleaved Forest
5 WATER
51 Streams & Waterways
52 Lakes
53 Reservoirs
54 Great Lakes
6 WETLANDS
61 Forested (wooded) Wetlands
62 Non-Forested (non-wooded) Wetlands
7 BARREN
71 Salt Flats (not applicable to Michigan)
72 Beaches & Riverbanks
73 Sand Other than Beaches
74 Bare Exposed Rock
75 Transitional Areas
79 Other
8 TUNDRA (not applicable to Michigan)
9 PERMANENT SNOW & ICE (not applicable to Michigan)
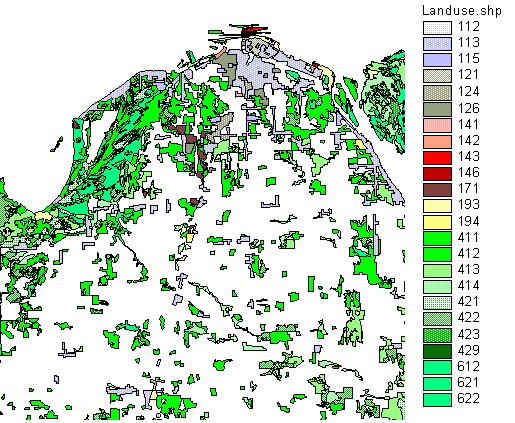
Level III is suitable for classifying images at scales ranging from 1:20,000 to 1:80,000. The categories are designed to be adaptable to the local needs of public agencies.
Level IV is most useful for airphotos at scales larger than 1:20,000. The categories are designed to be adaptable to the local needs of public agencies.
Level I,II, III and IV Classification Example
| 4 Forest Land (Level I) 42 Coniferous Forest (Level II) 421 Upland conifers (Level III) 4211 White pine predominates (Level IV) 4212 Red pine predominates (Level IV) 4213 Jack pine predominates (Level IV) 4214 Scotch pine predominates (Level IV) 4215 White spruce perdominates (Level IV) 4219 Other (Level IV) 422 Lowland conifers (Level III) 4221 Cedar predominates (Level IV) 4222 Black spruce predominates (Level IV) 4223 Tamarack Predominates (Level IV) 4224 Balsam fir-white spruce predominates (Level IV) 4225 Balsam fir predominates (Level IV) 4229 Other (Level IV) |
Michigan Land Use/Cover Classification
Limitations in Land Use / Land Cover Mapping
The classification level used for Land use and land cover mapping and the accuracy attainable is dependent on a number of important factors such as image scale, season, and interpretability.
Image Scale: the ability to classify a feature will vary with the image scale which affects the classification level that can be used.
Seasonal Variations: Vegetation characteristics vary with the season which affects the ease of interpretation.
Interpretability: classification of features should be repeatable between interpreters. The precise boundaries within and between classes may be gradational making this difficult to achieve.
Michigan Resource Inventory Program
This program was established to gather the best available information about the status of land and water resources and have it available for private and public use.
Several inventories of information were collected such as: Topographic Data, Land Use /Land Cover Inventory, Mineral Resource Inventory, Soil Survey Data, and Forest Inventory.
Each of these inventories form a computerized database which is accessible using Geographic Information Systems and represented as 'layers' or 'overlays' which can be queried and analysed.
Gersmehl: p. 67 - 98
Arnold: p. 36 - 49